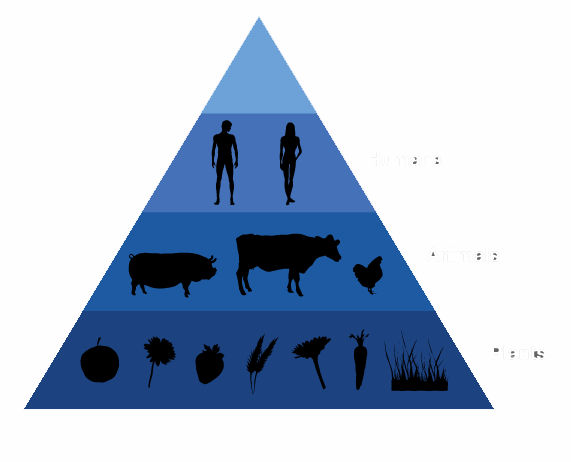
Food chain is the transfer of food energy through a series of bodies , which feeds each of the preceding and the following food .
Each chain begins with a vegetable producer or agency that is a body which " makes its own food " synthesizing organic substances from inorganic substances taken from the air and soil , and solar energy ( photosynthesis).
The other members of the chain are called consumers. One, who eats the producer, will be the primary consumer, which feeds on the latter are secondary consumer and so on. They are primary consumers, herbivores. They are secondary consumers, tertiary, etc. . . . Carnivores.
A final level in the food chain that corresponds to the decomposers. These act on the dead bodies , degrade and transform organic matter into inorganic matter again returning to the soil ( nitrates , nitrites , water) and atmosphere (carbon dioxide ) .
Each level of the chain is called a link.
In a food chain , each link gets the energy needed for life of the immediately preceding level ; and the producer gets the sun .. So the energy flows through the chain.
In this flow of energy a loss of it occurs in each transfer from one link to another , so a high level of consumer ( e.g. consumer 3ario ) receive less energy than a low (e.g. 1ario consumer).
Given this condition of power flow, the length of a string does not go beyond tertiary or quaternary consumer.
A food chain in the strict sense , has several disadvantages disappear if one link :
a) Disappear with him all these links as they will be without food.
b ) The immediately preceding level is superpoblará , for there is not the predator.
c ) the lower levels due to the above in a) and b unbalance ) .
d ) For these reasons food webs or food webs are more profitable than isolated chains.