Ecosystem called all interactions
that exist between living things and between them and the environment in which
they find themselves. By definition, the ecosystem is composed of elements
living (biotic) and non- living (abiotic). Within the first animals, plants,
algae, fungi, bacteria and protozoa are included. The abiotic factors are
water, soil, air, sunlight, weather factors, etc. For that reason it is important
to know the different relationships that exist between living things and their
environment. . Ecosystems are studied by analyzing the food chain, the cycles
of matter and energy flows. The importance of the ecosystem concept is that
“everything is related to everything."
Ecosystem called all interactions
that exist between living things and between them and the environment in which
they find themselves. By definition, the ecosystem is composed of elements
living (biotic) and non- living (abiotic). Within the first animals, plants,
algae, fungi, bacteria and protozoa are included. The abiotic factors are
water, soil, air, sunlight, weather factors, etc. For that reason it is important
to know the different relationships that exist between living things and their
environment. . Ecosystems are studied by analyzing the food chain, the cycles
of matter and energy flows. The importance of the ecosystem concept is that
“everything is related to everything."Ecosystems
Publicado por
ecosystems
 Ecosystem called all interactions
that exist between living things and between them and the environment in which
they find themselves. By definition, the ecosystem is composed of elements
living (biotic) and non- living (abiotic). Within the first animals, plants,
algae, fungi, bacteria and protozoa are included. The abiotic factors are
water, soil, air, sunlight, weather factors, etc. For that reason it is important
to know the different relationships that exist between living things and their
environment. . Ecosystems are studied by analyzing the food chain, the cycles
of matter and energy flows. The importance of the ecosystem concept is that
“everything is related to everything."
Ecosystem called all interactions
that exist between living things and between them and the environment in which
they find themselves. By definition, the ecosystem is composed of elements
living (biotic) and non- living (abiotic). Within the first animals, plants,
algae, fungi, bacteria and protozoa are included. The abiotic factors are
water, soil, air, sunlight, weather factors, etc. For that reason it is important
to know the different relationships that exist between living things and their
environment. . Ecosystems are studied by analyzing the food chain, the cycles
of matter and energy flows. The importance of the ecosystem concept is that
“everything is related to everything."Levels of Organization of Ecology
Publicado por
ecosystems
Ecology is a branch of
Biological Science that studies ecosystems. Have different levels of
organization that are ordered increasingly: Guy - species - population -
community - ecosystem - Biome - biosphere.
1 - Guy
it
is every living being present in nature. An individual is a horse, a tree, a
carnation, a man or bacteria.
2 - Kind
Are individuals interbreed and leave fertile offspring, as humans, cattle or
willows. There are cases where two individuals of different species can
reproduce, but their offspring are infertile.
3 - Population
Set of individuals living at the same time in the same place, are interrelated
and belong to the same species.
It
is the set of populations that live together in one place. That's why there is
a community in many plant and animal species. The community is also called the
biocenosis.
5 - Biome
It is a
group of ecosystems with some similar features concerning the uniform climate
and vegetation. In other words, a biome is a large area unit that encompasses
many ecosystems that develop under the same climate, and can be identified by
their uniform vegetation. It should be noted that a specific atmosphere is
accompanied by characteristic vegetation.
6 - Biosphere
It
is the part of the earth (water, air and soil) where conditions for life to
develop there. Or biosphere the biosphere is represented by all plants,
animals, fungi and microorganisms that inhabit the planet. It extends from the
deep ocean to a height in the atmosphere of about six kilometers from the level
sea.
Ecosystem Structure: Biotic and Abiotic Factors
Publicado por
ecosystems
When we refer to the biotic ecosystem structure talk about the parts or elements that compose it and the relationships between them to form a whole.
Biotic structure is determined by the various agencies or living things that make up the ecosystem and how they interact to give rise to different classes of organisms. In this sense, the biotic structure is based on power relations , resulting in three major categories of organisms :
1 ) producers ,
2 ) consumers
3 ) saprophytic decomposers.
Producers: Mainly related to organisms that have the ability to harness light energy from the sun to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen through the mechanism of photosynthesis. Furthermore, these organisms make their own food from the sugar molecules and other elements from the soil
Consumers: Consumers are characterized by obtaining energy producers or consumers of other organisms. In this category we can find a variety of microorganisms and macro-organisms . Within this category we can define different groups, depending on the source of obtaining energy. When the consumer eats primary producers are called primary consumers or herbivores, whereas when feeding on primary consumers called secondary consumers, or carnivores second order. Consumers can eat both plants and animals are considered omnivores. When consumers, plant or animal feed for a longer period of time from another plant or animal, is called parasite.
Saprophytes or decomposers of detritus: This category includes organisms that feed on detritus, dead plant material or corpses or animal feces. Here we find organisms such as earthworms, ants and beetles, fungi and bacteria also found.
Abiotic ecosystem structure is determined by the physical and chemical agents thereof. These agents largely determine the survival of the organisms in the ecosystem and their importance varies according to the environment to which we refer. The main actors are (Bernard & Wright, 1999):
• Rainfall pattern: amount and annual distribution and soil moisture
• Temperature: extremes of cold and heat, average
• Light: intensity
 • Wind: Speed
• Wind: Speed
• Chemical nutrients: phosphorus, nitrogen , sulfur
• PH: acidity
• Salinity: freshwater or saltwater
• Turbidity: The amount the light passing through the water column
• Soil texture: rocky or sandy
• Fire patterns
Each species , in particular each agency to respond in differential form factors ; There is a range of values within which the organism can carry out the fundamental processes of growth and reproduction , however , there is an optimum level for each factor or in which organisms function better.
Biotic structure is determined by the various agencies or living things that make up the ecosystem and how they interact to give rise to different classes of organisms. In this sense, the biotic structure is based on power relations , resulting in three major categories of organisms :
1 ) producers ,
2 ) consumers
3 ) saprophytic decomposers.
Producers: Mainly related to organisms that have the ability to harness light energy from the sun to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen through the mechanism of photosynthesis. Furthermore, these organisms make their own food from the sugar molecules and other elements from the soil
Consumers: Consumers are characterized by obtaining energy producers or consumers of other organisms. In this category we can find a variety of microorganisms and macro-organisms . Within this category we can define different groups, depending on the source of obtaining energy. When the consumer eats primary producers are called primary consumers or herbivores, whereas when feeding on primary consumers called secondary consumers, or carnivores second order. Consumers can eat both plants and animals are considered omnivores. When consumers, plant or animal feed for a longer period of time from another plant or animal, is called parasite.
Saprophytes or decomposers of detritus: This category includes organisms that feed on detritus, dead plant material or corpses or animal feces. Here we find organisms such as earthworms, ants and beetles, fungi and bacteria also found.
Abiotic ecosystem structure is determined by the physical and chemical agents thereof. These agents largely determine the survival of the organisms in the ecosystem and their importance varies according to the environment to which we refer. The main actors are (Bernard & Wright, 1999):
• Rainfall pattern: amount and annual distribution and soil moisture
• Temperature: extremes of cold and heat, average
• Light: intensity
 • Wind: Speed
• Wind: Speed• Chemical nutrients: phosphorus, nitrogen , sulfur
• PH: acidity
• Salinity: freshwater or saltwater
• Turbidity: The amount the light passing through the water column
• Soil texture: rocky or sandy
• Fire patterns
Each species , in particular each agency to respond in differential form factors ; There is a range of values within which the organism can carry out the fundamental processes of growth and reproduction , however , there is an optimum level for each factor or in which organisms function better.
Ratings Aencies
Publicado por
ecosystems
Since ancient times, scholars have tried to interpret Nature natural world seeking an order. Thus arises the need for sorting or classification of organisms and their appointment. The ratings therefore are explanatory of the relationships between living things hypotheses.
. Classification of five kingdoms
Kingdom Monera includes prokaryotes to unicellular living beings. Archaebacteria and eubacteria are.
. Classification of five kingdoms
Kingdom Monera includes prokaryotes to unicellular living beings. Archaebacteria and eubacteria are.
Protista a kingdom comprises two types of organisms: heterotrophic unicellular eukaryotic organisms with internal digestion (protozoa) and unicellular eukaryotes or multicellular talofíticos (no tissue) photosynthetic autotrophy (algae).
Kingdom Fungi includes a unicellular or multicellular eukaryotes talofítica organization of heterotrophic nutrition and external digestion (fungi) .
A Includes Vegetable multicellular eukaryotic organisms with differentiated tissues and nutrition photosynthetic autotrophic (plants).
A Includes Animals living multicellular eukaryotes with well-formed tissues, heterotrophic nutrition and internal digestion (animals).
Kingdom Fungi includes a unicellular or multicellular eukaryotes talofítica organization of heterotrophic nutrition and external digestion (fungi) .
A Includes Vegetable multicellular eukaryotic organisms with differentiated tissues and nutrition photosynthetic autotrophic (plants).
A Includes Animals living multicellular eukaryotes with well-formed tissues, heterotrophic nutrition and internal digestion (animals).
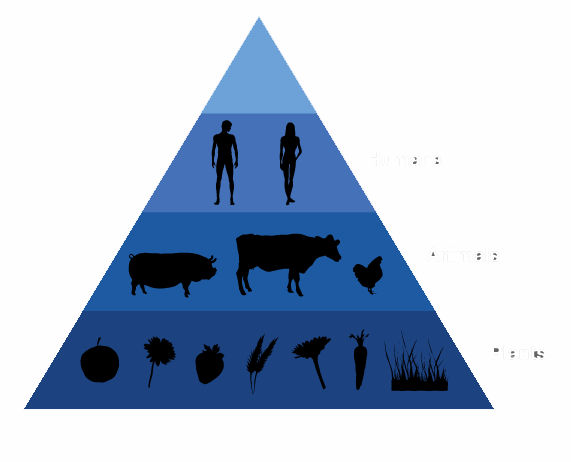
Food chain (trophic chain)
Publicado por
ecosystems
Food chain is the transfer of food energy through a series of bodies , which feeds each of the preceding and the following food .
Each chain begins with a vegetable producer or agency that is a body which " makes its own food " synthesizing organic substances from inorganic substances taken from the air and soil , and solar energy ( photosynthesis).
The other members of the chain are called consumers. One, who eats the producer, will be the primary consumer, which feeds on the latter are secondary consumer and so on. They are primary consumers, herbivores. They are secondary consumers, tertiary, etc. . . . Carnivores.
A final level in the food chain that corresponds to the decomposers. These act on the dead bodies , degrade and transform organic matter into inorganic matter again returning to the soil ( nitrates , nitrites , water) and atmosphere (carbon dioxide ) .
Each level of the chain is called a link.
In a food chain , each link gets the energy needed for life of the immediately preceding level ; and the producer gets the sun .. So the energy flows through the chain.
In this flow of energy a loss of it occurs in each transfer from one link to another , so a high level of consumer ( e.g. consumer 3ario ) receive less energy than a low (e.g. 1ario consumer).
Given this condition of power flow, the length of a string does not go beyond tertiary or quaternary consumer.
A food chain in the strict sense , has several disadvantages disappear if one link :
a) Disappear with him all these links as they will be without food.
b ) The immediately preceding level is superpoblará , for there is not the predator.
c ) the lower levels due to the above in a) and b unbalance ) .
d ) For these reasons food webs or food webs are more profitable than isolated chains.
Biome
Publicado por
ecosystems
The Biomes will be defined primarily by factors such as plant structures , leaf types and the spaces between the plants, because the biomes are identified primarily by particular patterns of ecological succession and vegetation. Moreover, the biomes are classified into terrestrial Biomes , Biomes Marine and freshwater , but are mostly known by local names by which they are commonly designated , grasslands, shrublands and sheets , among others. As long as it we mentioned above , the weather is the main decision maker and definer of a biome and especially in determining the distribution of terrestrial biomes , depending on the same the following issues : the latitude to define the types arctic , boreal, tropical, subtropical and temperate ; determine the moisture wet types , semi-wet , arid and semiarid and finally the altitude, which is what defines the montage , montage , alpine and alvar types . Large and major biomes of the world.
The rainforest, also called as tropical rain forest is characterized by its density and tropical climate in which abundant rainfall and the average temperature is usually high Undoubtedly this is the most extensive and important ecosystem of our planet and owns a wealth and variety of the species presented.
____________________________________________________________________________
Savannah
 Meanwhile, Savannah is an ecosystem that is characterized by the presence of trees and shrubs , while the trees produce low coverage because they are rather small and sparse trees. It is characterized by its dry climate being a transition zone between the forest and the semi-desert. Mostly found in the savannas in tropical and subtropical regions that have dry tropical climates.
Meanwhile, Savannah is an ecosystem that is characterized by the presence of trees and shrubs , while the trees produce low coverage because they are rather small and sparse trees. It is characterized by its dry climate being a transition zone between the forest and the semi-desert. Mostly found in the savannas in tropical and subtropical regions that have dry tropical climates.____________________________________________________________________________
Steppe
The steppe is a biome consisting of flat land with herbaceous vegetation in which extreme weather and low rainfall , which can not exceed 250 mm in the year prevail. The steppes be found far from the seas and as we said, with a huge variation in temperature in both summer and winter. The vegetation is rather low , scrub type . The soil is rich in minerals and low in organic matter.
____________________________________________________________________________
Temperate Rainforest
The temperate forest biome is the greater diversity of our planet , however, and unfortunately the indiscriminate use of the human being from their trees , for firewood , for building, among others, has led to its decline and in some cases their loss.
____________________________________________________
Tundra
The tundra extends around the north and south poles , being case its freezing temperatures and frozen ground. Virtually no green trees and the ground may be covered with mosses and lichens It should be noted that there are other similes in the Tundra biomes in the high mountains , as in the case of Tibet
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)